The Step-by-Step Process of Conducting an Arc Flash Analysis
Arc flash hazard calculations are a safety mechanism used to determine the chances of arc flashes in workplaces, with the aim of minimizing their occurrences. Arc flashes, which are powerful, can lead to serious burns and sometimes death, which means that a thorough evaluation is required for employees to be safeguarded.
An arc flash assessment assists organizations in determining the risks posed within electric systems and allows for safety measures to be taken. Presented in the following sections is a guide to performing an arc flash assessment to minimize risk to the workers and guarantee the stability of the electrical system.
1. Gather Necessary Electrical Data
The initial process in carrying out an arc flash analysis involves gathering all the required information with regards to the existing electrical system. This includes details regarding transformers, circuit breakers, switch gears, and panel boards. The following are details are taken:
- Voltage levels
- Current ratings
- Protective device settings
- Equipment configuration
The arc flash analysis is dependent on these values, hence the need to ensure that accurate and thorough data is collected.
2. Conduct a Short Circuit Test
The short circuit study is done with the aim of identifying available fault currents in the system. With the help of a specialized software or using tables given in IEEE 1584, it is possible to determine fault currents in the electrical system.
3. Conduct a Coordination Study
The next step of the arc flash analysis is the coordination study, in which the operations of the devices in the system like fuses and circuit breakers and faults are looked at. This allows proper coordination so that the correct device will be triggered to break a fault current, reducing further damage and increasing safety.
4. Calculate Incident Energy
Employing the collected electrical data and outcomes from the short circuit and coordination studies, engineers can determine the degree of the incident energy in various points of the system. This energy is computed based on standards given by the IEEE 1584 and formulas depending on various conditions such as voltage, fault current, and working distance, among others.
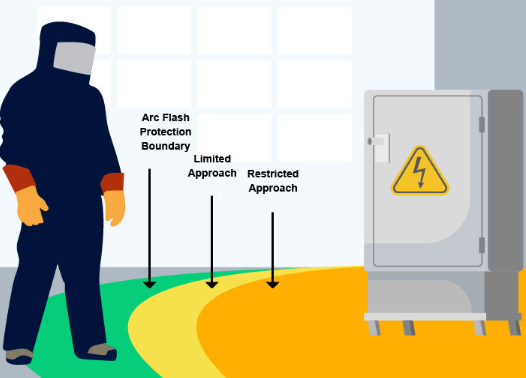
5. Determine Arc Flash Boundaries
Arc flash boundaries refer to the areas where workers can safely conduct operations around electrical equipment. Based on the calculated incident energy, a boundary is set and from that boundary, areas that require specific body gear are designated. There is little risk of being injured by an arc flash once the above boundary is crossed.
6. Label Equipment and Offer Suggestions
Once the incident energy and arc flash boundaries are defined, the equipment clearly needs to be marked with proper arc flash hazard levels and/or required personal protective equipment. Labels should meet the requirements of the local legislation and give clear instructions to the employees concerning the danger level. Furthermore, the findings obtained should be used for coming up with solutions on how to enhance the electrical safety more—for instance, replace or upgrade the equipment, change the settings of the protective devices or train the human resource on different aspects of electrical safety.





