What Are The Different Types Of Pedestrian Crossings?

Pedestrian intersections and crossings are important components of urban infrastructure. This ensures the safety of people walking through busy streets. Understanding pedestrian crossings, both for pedestrians and drivers, is vital to maintaining safety and efficiency. Driving instructors often stress this knowledge when teaching new drivers. This article explores different types of pedestrian crosswalks, their features and how they help to improve road safety.
- Zebra Crossings
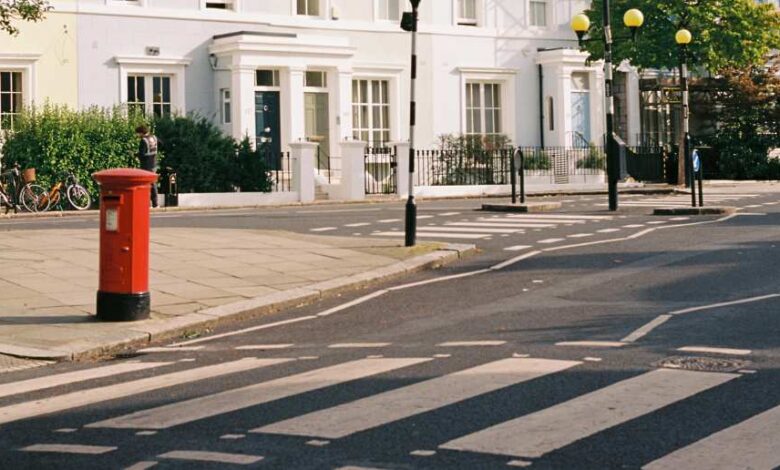
Zebra crosses have become the most popular type of pedestrian crosswalk. The crossings have wide, white stripes painted in the middle of the road that looks like a pair of stripes on a horse. These crossings lack traffic lights. Instead, they rely on drivers’ willingness to yield to pedestrians.
Features:
- Location: Most commonly found near residential areas, schools, shopping districts, and other public places.
- Signs: These are usually indicated with poles striped in black and white, often with flashing yellow lights.
Safety Advice: Always slow down your vehicle when approaching the zebra crossing.
- Pelican Crossings
Pelican Crossings Pedestrian Light Controlled Crossings are signal-controlled intersections at which pedestrians have to press a switch to activate the traffic light. The pedestrian crossing lights will turn red as soon as the vehicles pass.
Features:
- Location: Most commonly found in urban zones with heavy foot traffic.
- Signals Traffic lights are changing from green to amber and then red. A flashing “green man” signal tells pedestrians to stop crossing. Those already crossing are allowed to finish.
- Rules: Drivers have to stop when the light flashes red and proceed with caution whenever the light flashes amber.
Safety Tips: Cross the street only when there is a green light and all cars have stopped.
- Puffin Crossings
Puffin Crossings (Pedestrian Friendly Intelligent Crossings – PUIC) are a modern version of the pelican crosses. Sensors are used to detect pedestrians waiting to cross. If necessary, the crossing period is extended.
Features:
- Location: It is found in areas that have varied pedestrian traffic.
- Technology Sensors and cameras that detect pedestrian motion adjust the signal timing to match.
- Green Man: Similar signals to those at pelican crosswalks, without the flashing ‘green man’ signal. The red signal for vehicles will remain on until the pedestrians have successfully crossed.
- Safety Advice: If you are a pedestrian, press and hold the button until the green-man signal appears. Make sure that all vehicles have stopped.
- Toucans Crossings
Toucan crosses are intended for pedestrians as well as cyclists to use simultaneously. They are typically found near cycling paths.
Features:
- Location: It is commonly located near shared-use paths and parks.
- Crossing Signals: A traffic light system controls the crossing. Similar to pelican crossings with cyclists added.
- Rules A cyclist can cross the street without getting off their bike, and pedestrians need to follow the green signal.
Safety Advice: Bicyclists and pedestrians need to be aware and use the crosswalk simultaneously without blocking one another.
- Pegasus Crossings
Pegasus crosses, along with pedestrians and bicyclers, are specifically designed to accommodate horse riders. These crossings include higher-mounted button pushes to accommodate horses.
Features:
- Location: Commonly found near equestrian centres and bridle routes.
- Signs: Similar in appearance to the crossing of toucans but includes additional signals for horse riders.
- Rules Horse-riders, pedestrians, and bicyclists should follow the appropriate signals when crossing the road.
Safety Advice: Drivers must be cautious and reduce their speed when approaching a pegasus crossing because horses can be unpredictable.
- School Crossings
School Crossings, also called “lollipop crosswalks”, – are supervised by crossing attendants who use stop signs to halt the traffic, allowing children to cross safely.
Features:
- Location: Location near school and educational institutions
- Control: The crossing guards, or lollipop men and women, are equipped with handheld stop signs.
- Rules: When the crossing officer signals, drivers must stop.
Safety Tips: Approach crossings near schools with caution. Be prepared to stop at any time, but especially when school is in session.
Conclusion
Understanding how to cross the road safely is crucial. A driving instructor near you home will stress that each type of pedestrian crossing comes with its own set of rules and features designed to keep pedestrians safe. These systems are designed to work together, regardless of whether they’re the simple zebra-crossing or the high-tech puffin-crossing. These guidelines are for both pedestrians and drivers to follow to ensure road safety.